BLOG

Don’t get hacked: Why VAPT is your cybersecurity superpower
Brian Borysewich, CISO at C8 Secure explores why a cybersecurity assessment business focus is critical for evaluating and protecting an organization’s cybersecurity infrastructure.
 In today’s digital world, cyber threats lurk around every corner. From sneaky malware to sophisticated ransomware, attackers are relentless. So, how do you stay one step ahead? The answer lies in cybersecurity assessments, with Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Testing (VAPT) leading the charge. At C8 Secure, we’re passionate about helping businesses like yours fortify their defenses. Let’s dive into why VAPT and risk assessments are game-changers for securing your organization.
In today’s digital world, cyber threats lurk around every corner. From sneaky malware to sophisticated ransomware, attackers are relentless. So, how do you stay one step ahead? The answer lies in cybersecurity assessments, with Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Testing (VAPT) leading the charge. At C8 Secure, we’re passionate about helping businesses like yours fortify their defenses. Let’s dive into why VAPT and risk assessments are game-changers for securing your organization.
What’s a cybersecurity assessment?
Think of a cybersecurity assessment as a full-body scan for your IT systems. It’s a deep dive into your network, applications and processes to uncover vulnerabilities before hackers do. These assessments aren’t just about finding weaknesses, they’re about giving you a clear roadmap to fix them.
For businesses seeking VAPT, this is your proactive shield. It combines vulnerability assessments (finding the cracks) with penetration testing (testing if those cracks can be exploited). Paired with broader cybersecurity risk assessments, VAPT ensures your organization is ready to face any threat.
Part 1: VAPT – Your frontline defense
Imagine hiring an ethical hacker to break into your systems, except they’re on your side. That’s VAPT in a nutshell. It’s a systematic, hands-on approach to identifying and patching security gaps before they become headlines.
How does VAPT work?
VAPT is like a cyber obstacle course, testing every nook and cranny of your infrastructure. Here is the breakdown:
We map out your systems, applications and network to identify potential entry points.
- Vulnerability assessment
- Scan for weaknesses and misconfigured servers using automated tools and manual expertise, identifying outdated software and risky code
- Penetration testing
- Simulate real-world attacks to exploit vulnerabilities and determine how far an attacker can go
- Reporting
- Receive a detailed report with prioritized risks, exploitability insights and step-by-step remediation advice
This process isn’t a one-and-done. Regular VAPT keeps your defenses sharp as threats evolve.
Why VAPT is non-negotiable for your cybersecurity posture
- Catch issues early
- Find and fix vulnerabilities before attackers exploit them
- Test real-world scenarios
- Simulate hacker tactics through penetration testing to understand your cybersecurity posture
- Stay compliant
- Comply with industry regulations (finance, healthcare, government) by conducting regular VAPT
- Protect your reputation
- Protect customer trust by preventing breaches with proactive VAPT
VAPT best practices
To get the most out of VAPT, follow these tips:
- Scan regularly
- New vulnerabilities pop up daily. Schedule recurring assessments
- Prioritize fixes
- Focus on high-risk issues first to maximize impact
- Verify remediation
- After patching, retest to confirm the fix worked
- Integrate with DevOps
- Embed VAPT into your software development lifecycle for secure coding from the start
Part 2: The power of cybersecurity risk assessments
While VAPT zooms in on technical vulnerabilities, cybersecurity risk assessments take a broader view. They evaluate your entire security posture, controls, policies, processes and people to identify risks and gaps.
Why risk assessments matter
Risk assessments are like a strategic playbook for your cybersecurity team. Here’s what they deliver:
- Spot hidden gaps
- Uncover weaknesses in policies, employee training, or third-party integrations
- Get actionable fixes
- Receive clear recommendations to shore up defenses
- Boost resilience
- Strengthen your ability to withstand internal and external threats
- Stay proactive
- Anticipate risks before they become incident
- Build trust
- Show customers, partners and regulators you take cybersecurity seriously
Real-world impact
Imagine discovering that a forgotten server is exposing sensitive data, or that your team’s passwords are weak. A risk assessment catches these issues, helping you fix them before they’re exploited. For example, one of our healthcare clients used a risk assessment to identify outdated encryption protocols, enabling them to upgrade before a compliance audit.
Why choose C8 Secure?
At C8 Secure, we specialize in VAPT and cybersecurity risk assessments for industries such as finance, healthcare, government, media and technology. Our certified experts combine cutting-edge tools with hands-on techniques to deliver results you can trust.
What sets us apart
- Tailored assessments
- Benefit from a customized approach to align with your industry and infrastructure requirements
- Comprehensive reports
- Receive detailed, prioritized findings accompanied by actionable remediation steps
- Regulatory expertise
- Ensure compliance with relevant regulatory standards
- Ongoing support
- Work with experts every step of the way, from assessment to remediation
Our clients range from banks to tech start-ups and rely on us to keep their systems secure and their data safe. With C8 Secure, you’re not just getting a service – you’re gaining a partner in cybersecurity.
Ready to secure your future?
Cyber threats aren’t slowing down, but neither are we. C8 Secure offers multi-layered solutions to protect your digital assets, from VAPT to advanced threat detection and response. Whether you are a small business or a global enterprise, we are here to support you.
Take the first step
For more information on how C8 Secure can support your cybersecurity initiatives, email info@c8secure.com or download the cybersecurity assessment services brochure.
Don’t wait for a breach to act. With C8 Secure, you can assess, adapt and secure your organization for a safer tomorrow.
Let’s make cybersecurity your superpower.
DOWNLOAD BROCHURE
For more information, please download our solutions brochure
Related content: C8 Secure in the Philippines
TESTIMONIAL
Philippine National Bank – Customer Spotlight
Hear from Roland Oscuro, FSVP, CISO, Philippine National Bank, who discusses his company’s partnership with C8 Secure, providing SOC services to the company.
C8 Secure - Philippine National Bank - Customer Spotlight
EVENT
C8 Secure CIO Philippines Summit 2024
Our C8 Secure team hosted a Cybersecurity Summit gathering the brightest minds, industry leaders, and executives from top organizations.
C8 Secure CIO Philippines Summit 2024

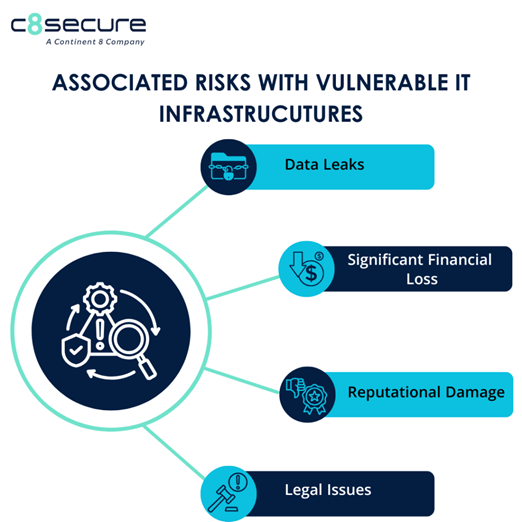





 In this Q&A, Gina expresses her enduring passion for cybersecurity, the challenges and opportunities she encounters with an expanding SOC team and platform and her unique insights on C8 Secure’s evolving SOC journey.
In this Q&A, Gina expresses her enduring passion for cybersecurity, the challenges and opportunities she encounters with an expanding SOC team and platform and her unique insights on C8 Secure’s evolving SOC journey.

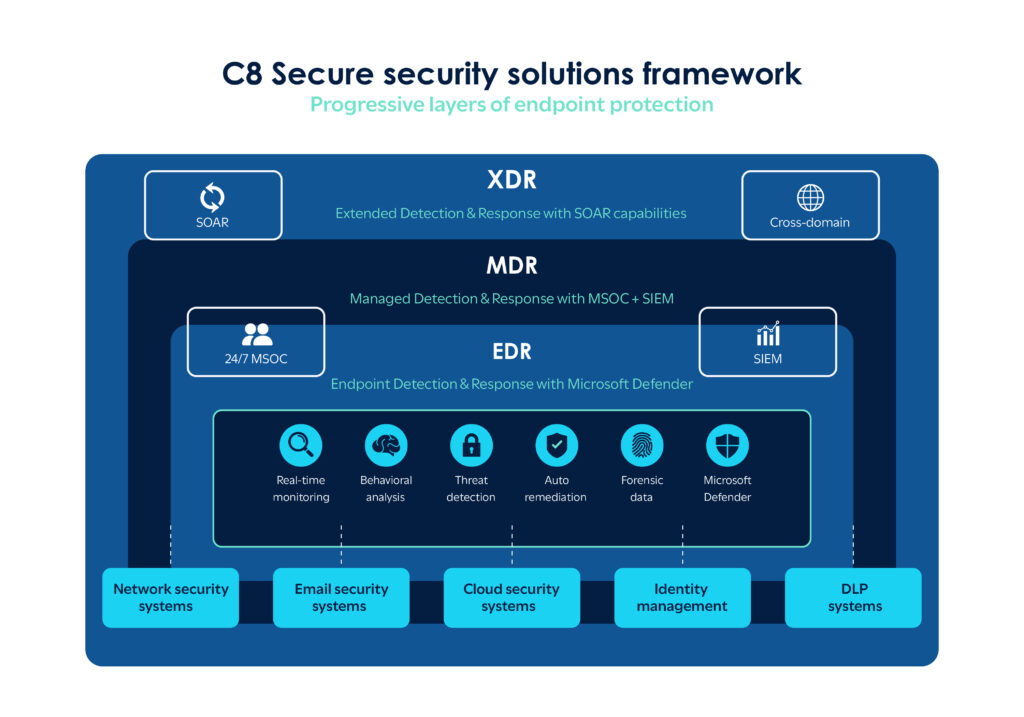
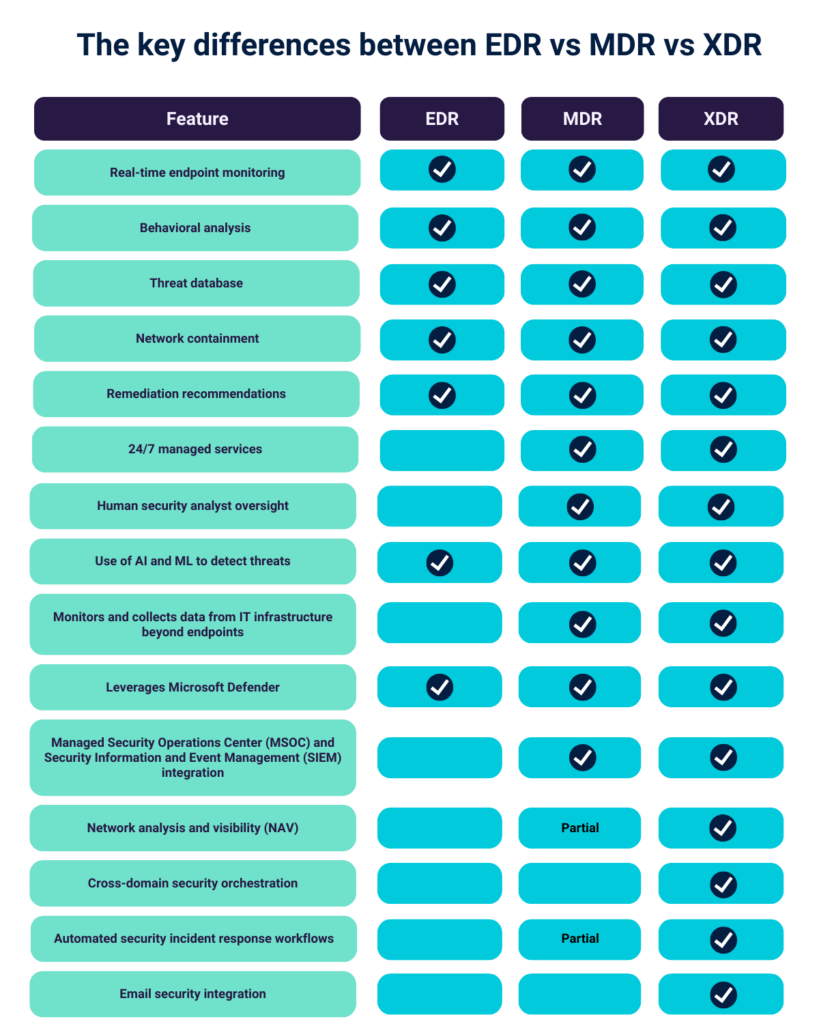
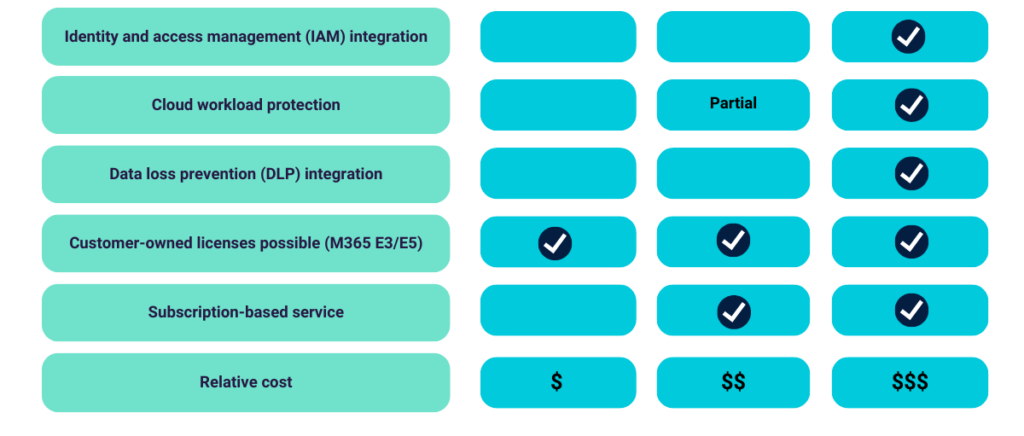









 In this blog, Craig Lusher, Product Principal at C8 Secure, explores how Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) platforms and Security Operations Centers (SOCs) allow organizations to adapt to emerging threats, maintain a robust cybersecurity posture and meet regulatory compliance.
In this blog, Craig Lusher, Product Principal at C8 Secure, explores how Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) platforms and Security Operations Centers (SOCs) allow organizations to adapt to emerging threats, maintain a robust cybersecurity posture and meet regulatory compliance.