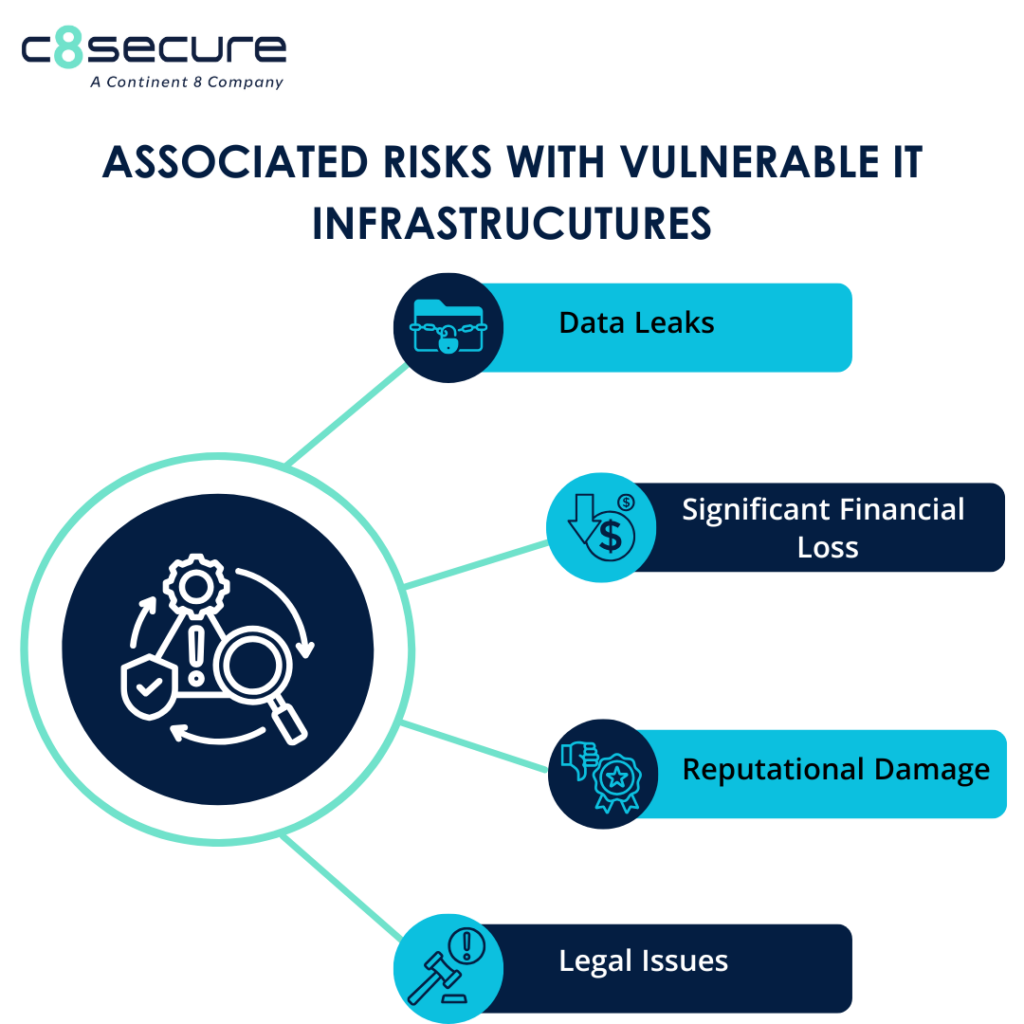
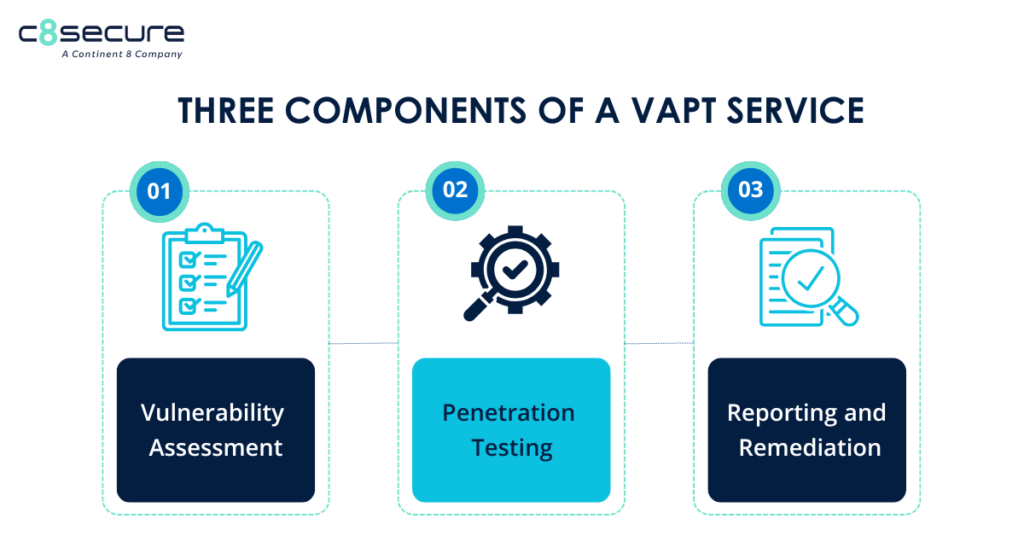
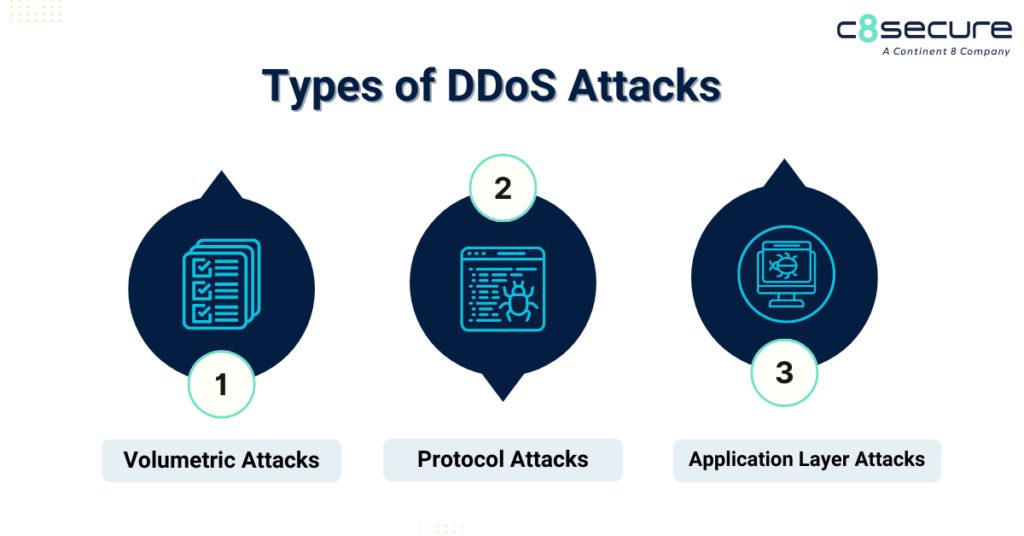
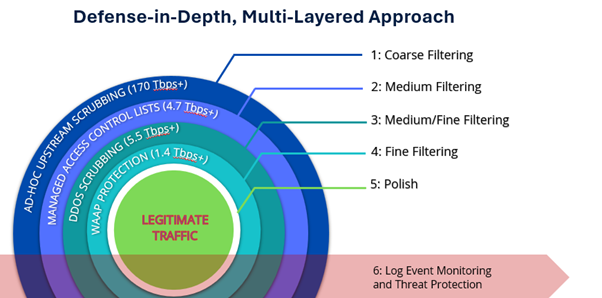
With the rapid evolution of technology, robust cybersecurity is vital for enterprises to protect sensitive information and systems from a range of cyber threats, including hacking, data breaches and malware attacks. As technology advances, so do the methods used by cyber criminals, necessitating the implementation of protective cybersecurity measures.
 In this blog, Craig Lusher, Product Principal at C8 Secure, explores how Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) platforms and Security Operations Centers (SOCs) allow organizations to adapt to emerging threats, maintain a robust cybersecurity posture and meet regulatory compliance.
In this blog, Craig Lusher, Product Principal at C8 Secure, explores how Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) platforms and Security Operations Centers (SOCs) allow organizations to adapt to emerging threats, maintain a robust cybersecurity posture and meet regulatory compliance.
What is SIEM?
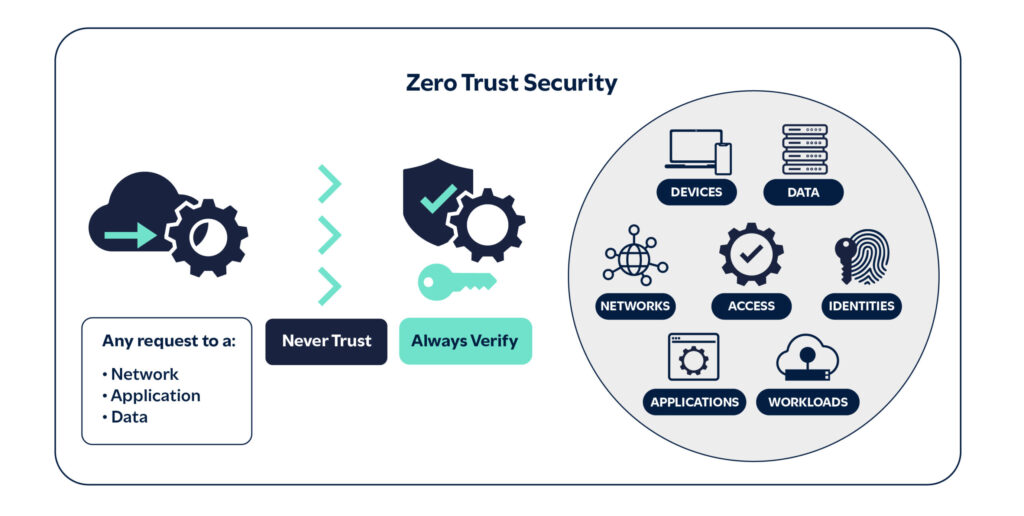
SIEM solutions consolidate security monitoring across an organization’s diverse technology stack, enabling SOC engineers to detect and respond to threats through a unified management interface. SIEM solutions serve as the central hub of an organization’s security system, collecting and normalizing security logs and events from various IT sources including network devices, servers and security systems. They provide a central register for all security events and logs, performing event correlation, threat enrichment and analysis, filtering out informational events and promoting true security events and threats, helping organizations protect their systems from attacks and breaches.
What is SOC?
A SOC, or Managed Security Operations Center (MSOC), such as those offered by C8 Secure and Continent 8 Technologies, is a dedicated team that focuses on safeguarding the company’s systems from security threats. Utilizing various tools, such as a SIEM system, they watch over the company’s computer systems, spot any problems or attacks and respond to them quickly. The SOC functions as a cybersecurity team, ensuring everything is running smoothly and securely.
SIEM vs. SOC: the role of SIEM in SOC
SIEM systems are integral in SOC cybersecurity, offering SOC teams with a holistic view of their cybersecurity events.
To begin, the SIEM system correlates and analyses the aggregated security data from internal sources and external threat intelligence to identify any unusual or suspicious activities that could indicate a potential security issue. Upon detection, it promptly alerts the SOC team, enabling them to address the issue swiftly.
In the event of an incident, the SIEM system provides comprehensive information that assists SOC analysts in understanding the nature and severity of the threat. This insight aids in effective response and helps prevent future occurrences.
Additionally, SIEM systems support compliance efforts by generating reports and maintaining logs that demonstrate the organization’s adherence to necessary regulations. These systems are indispensable for managing security incidents and events, facilitating efficient monitoring, detection and management of security challenges by SOC teams.
Can you have a SOC without a SIEM?
Operating a SOC without a SIEM system would be quite challenging. A SIEM system provides the centralized tool required to gather and interpret security data, which is crucial for effectively preventing, detecting, investigating and responding to threats. While a SOC might use other tools and methods, SIEM systems are integral for streamlining these processes and ensuring comprehensive cybersecurity management. SIEM systems employ advanced analytics and automation to filter and prioritize security alerts, preventing the cognitive overload, or alert fatigue, that occurs when SOC engineers manually process a constant barrage of security logs. This intelligent filtering not only reduces the risk of human error and missed security events but also optimizes operational costs by allowing SOC engineers to focus their expertise on critical threat analysis and incident response rather than routine log review. The result is more efficient resource allocation and enhanced security effectiveness.
Keys to effective SIEM and SOC strategies
A successful SIEM and SOC strategy begins with defining clear objectives and goals for each system. Essential components of effective SIEM and SOC strategies include:
• Comprehensive data collection for the effectiveness of both SIEM and SOC systems. SIEM requires gathering and standardizing data from various sources, such as network devices and servers. The SOC then integrates this data to ensure a complete cybersecurity overview is maintained. The more sources and context provided to the SIEM, the better it will perform.
• Real-time monitoring and alerting by SIEM are essential for quickly identifying issues. The SOC also must respond to these alerts quickly, prioritizing and addressing potential threats effectively. The SIEM system’s advanced correlation and analysis capabilities help identify complex attack patterns, which SOC analysts use to understand and respond to threats. Security Orchestration and Automated Response (SOAR) technology enhances security operations by automating threat response within carefully defined parameters. By implementing pre-approved automated response protocols, SOAR significantly reduces incident response times while increasing the complexity and cost for potential attackers. This automated capability operates within a precise framework of predefined actions, allowing the SIEM system to execute security decisions autonomously yet safely. The integration of SOAR not only accelerates threat mitigation but also enables SOC analysts to focus on more complex security challenges that require human expertise and strategic thinking.
• SIEM should facilitate incident response by surfacing valuable data from the billions of events it may contain, while the SOC needs clear steps, playbooks, for handling and recording incidents – these can be customized to fit company processes and culture. SIEM makes compliance and reporting easier by automating these tasks, and the SOC ensures compliance with regulatory rules.
• Regular updates to the SIEM system for optimal performance, and the SOC should continually review and enhance its operations. Equally important is ongoing staff training, ensuring SOC analysts are well-versed in best practices to use the SIEM effectively.
• The SIEM system’s threat intelligence capabilities should be both sophisticated and multi-faceted. It must effectively ingest, evaluate and prioritize threat data from diverse sources, creating a comprehensive security perspective. This includes correlating internal intelligence gathered from customer systems with external threat feeds, industry-specific security data and intelligence collected from dark web monitoring and other specialized sources. This multi-layered approach to threat intelligence enables more accurate risk assessment and more effective security response.
• Effective communication within the organisation regarding security events, along with collaboration with IT and other teams, is crucial for effective cybersecurity management.
• Lastly, using vendor support and engaging with the cybersecurity community can provide valuable insights and help maintain a strong SIEM and SOC strategy.
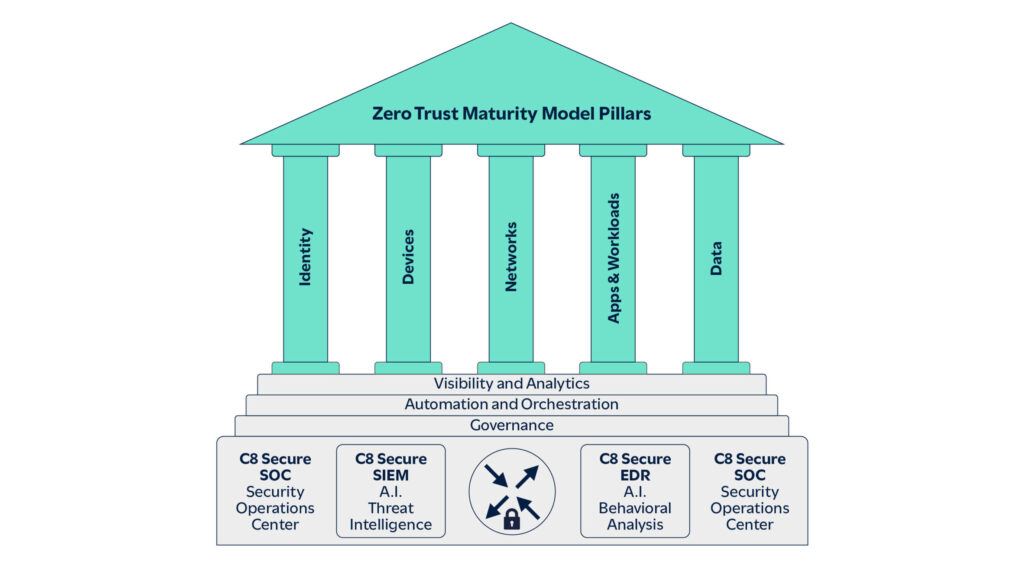
C8 Secure’s SIEM and MSOC approach
C8 Secure offers a comprehensive SIEM and Managed SOC solution that addresses critical cybersecurity challenges. This platform provides centralized visibility of your entire infrastructure, coupled with 24/7 expert monitoring and rapid threat detection and response, ensuring regulatory compliance while allowing maintaining a robust cybersecurity posture.
Our SIEM and MSOC solution consists of the following key service components:
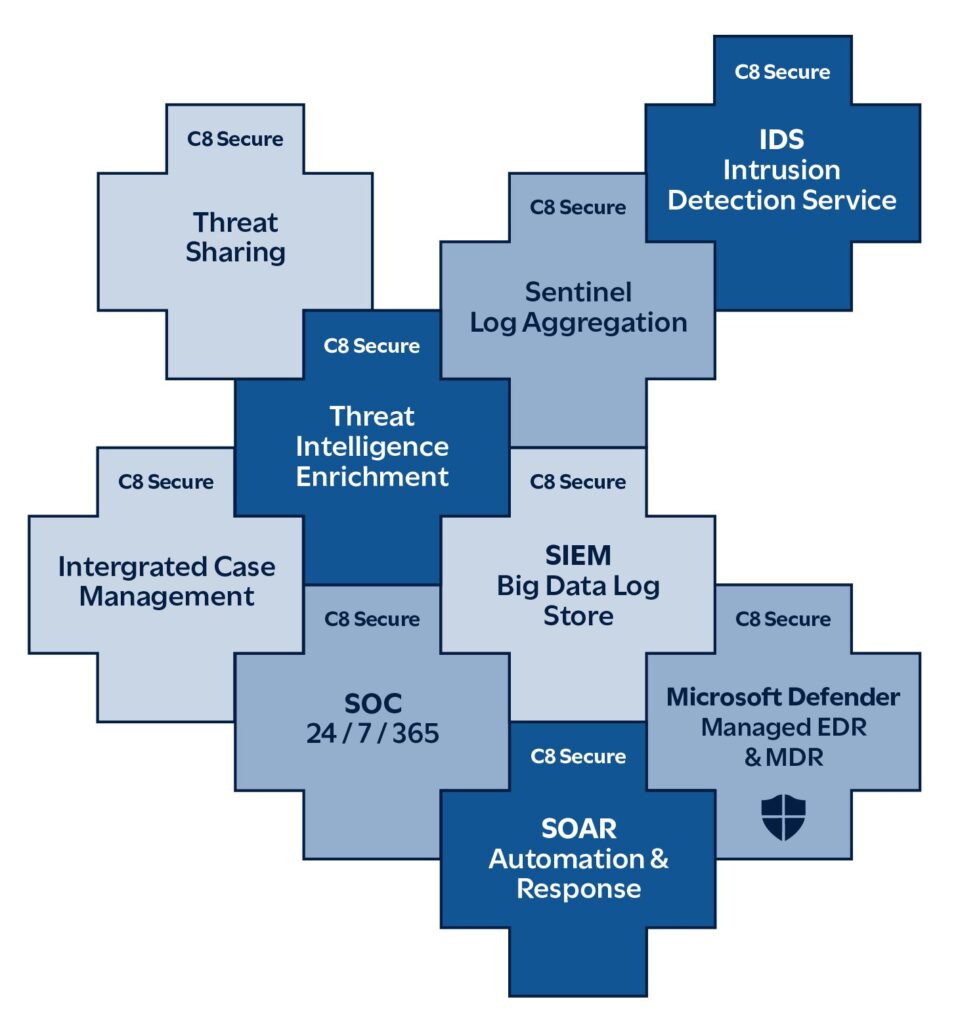
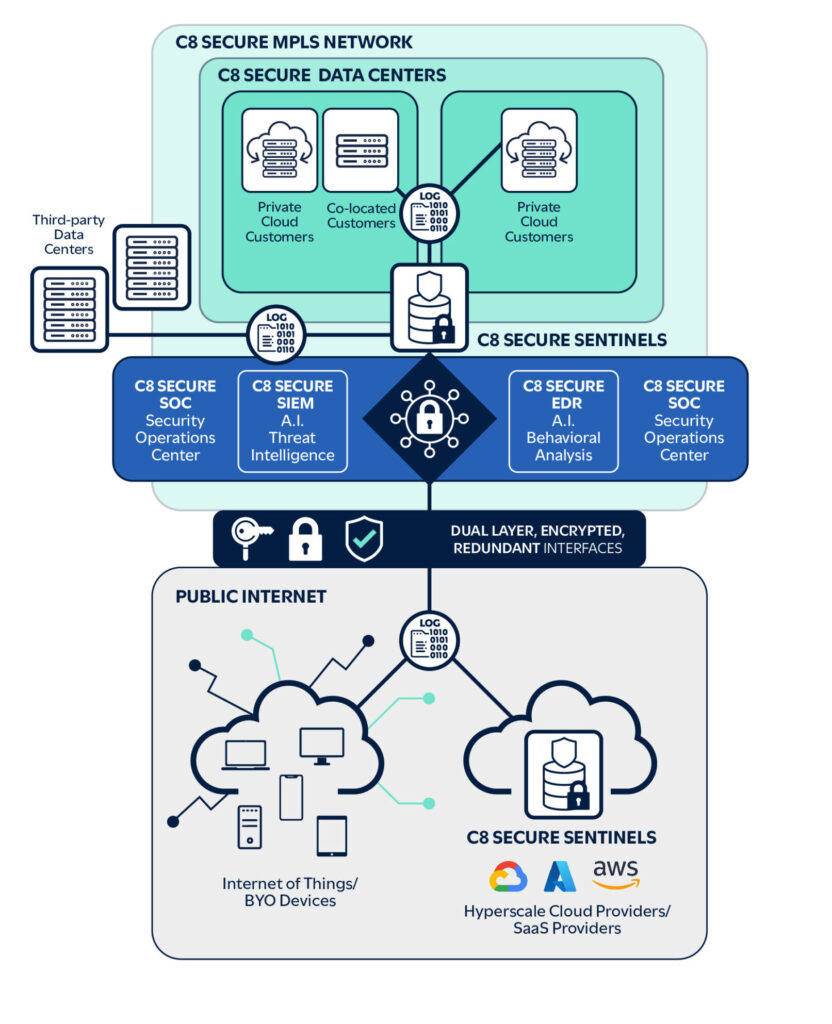
C8 Secure’s SIEM platform is a comprehensive, multi-tenant solution that gathers and correlates security data across a customer’s infrastructure. Enhanced by AI-driven SOAR and correlation capabilities with integrated threat intelligence tools, it delivers advanced analytics and automated incident response workflows. The platform is built for high performance, scalability and real-time threat detection, ensuring rapid identification and resolution of security incidents.
C8 Secure’s MSOC solution is a fully managed, multi-tenant service offering real-time security monitoring and incident response for customers. Following the NIST framework, it leverages our sophisticated SIEM platform to collect and analyse security alerts, offering customers actionable insights and remediation strategies through tailored playbooks. By outsourcing security operations to Managed Security Service Providers (MSSPs) such as C8 Secure, customers can focus on their core business while benefiting from the expertise of C8 Secure’s 24/7/365 global SOC team.
C8 Secure’s Sentinel managed device is deployed within the customer’s network, aggregating logs and events from various systems, normalizing them and preparing the data for secure transmission to the SIEM. It utilizes encryption to ensure data integrity and privacy, compressing and deduplicating data to optimize performance. Sentinel enhances security visibility by enabling seamless data collection and forwarding.
C8 Secure’s Incident Response System integrates directly into C8 Secure’s SIEM to streamline incident response processes. It provides a centralized platform for managing and tracking security incidents from detection to resolution, with built-in automation for workflows and playbooks. By enabling collaborative responses and providing real-time data sharing, it significantly improves incident resolution times while enhancing post-incident analysis and reporting.
C8 Secure’s Cyber Threat Intelligence Service serves as a structured repository for aggregating, analysing and sharing cyber threat intelligence. It allows organizations to collect data on threats, actors and campaigns, helping security teams anticipate and mitigate potential attacks. Through its powerful visualization tools, the service enhances situational awareness and enables proactive threat detection.
C8 Secure’s Security Orchestration and Automated Response (SOAR) tool, implemented within C8 Secure’s SIEM, provides a no-code automation platform for orchestrating and automating security workflows. Its drag-and-drop interface simplifies the creation of complex incident response processes, reducing manual effort and improving efficiency. With pre-built templates and over 2,000 app integrations, it enables quick deployment of automated responses, ensuring consistent handling of security incidents.
C8 Secure’s Threat Analysers and Responders are automation tools integrated into C8 Secure’s SIEM that enrich security events with threat intelligence from multiple sources. With over 100 analysers, they provide critical context for observables such as IPs and URLs, supporting faster decision-making during investigations. These tools enhance threat detection and response by simplifying data analysis and improving the quality of incident responses.
C8 Secure’s Intrusion Detection System (IDS), combined with our proprietary C8 Secure Sentinel platform, provides advanced network security monitoring, threat detection and response capabilities, delivering unparalleled visibility and security throughout your entire network infrastructure.
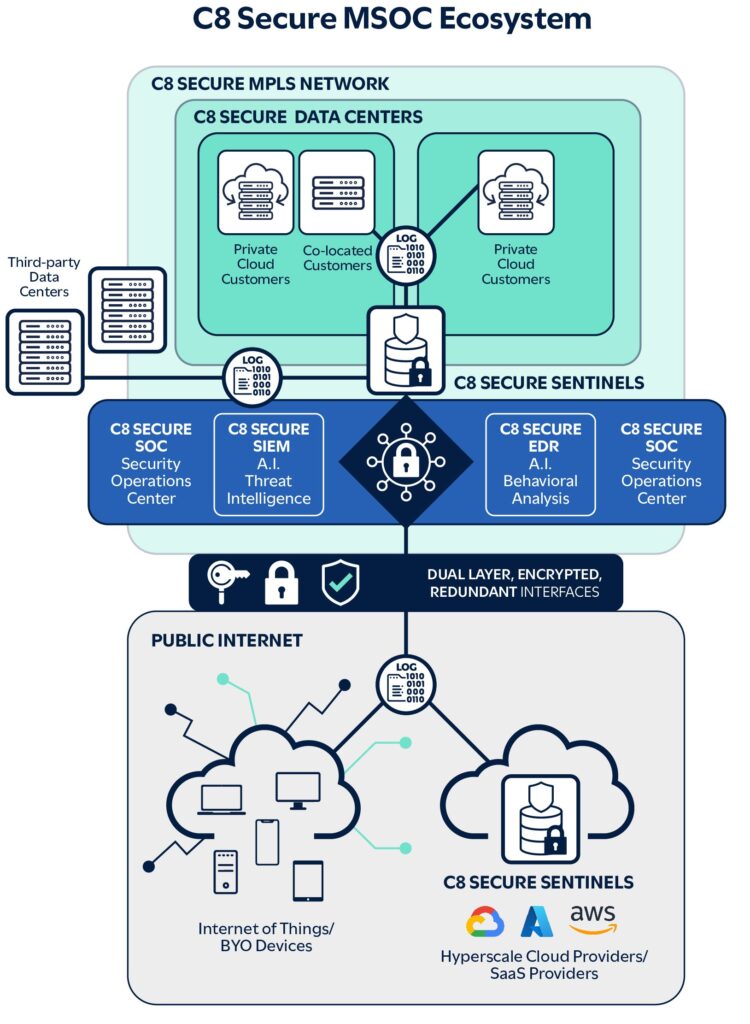
SIEM and MSOC – cybersecurity essentials
SIEM and MSOC services deliver significant cybersecurity enhancements through real-time monitoring, detection and response. This proactive approach aids in the early identification and mitigation of threats by collecting, analysing and correlating data from across a customer’s network with other ongoing security events. Collaborating with MSSPs also guarantees access to a dedicated team of SIEM and MSOC specialists who work closely with your IT team, providing playbooks and optimal risk mitigation strategies to address specific exploits or vulnerabilities, thereby ensuring optimal cybersecurity posture.
Cybersecurity solutions for a safer tomorrow
C8 Secure provides comprehensive, multi-layered threat prevention, detection and response solutions to secure your organization’s digital assets in the face of evolving cyber threats. For more information on how C8 Secure can support your cybersecurity initiatives, email info@c8secure.com or fill out our Contact Us page.








 Cybersecurity has always been a game of cat and mouse. For years, “zero-day” threats have kept cybersecurity teams on edge – these are vulnerabilities that attackers exploit before anyone even knows they exist. These threats leave no time for preparation, hence their name. But now, the game is changing, and not for the better. With artificial intelligence (AI) in the mix, zero-day dangers are evolving into something far more alarming: “zero hour” threats.
Cybersecurity has always been a game of cat and mouse. For years, “zero-day” threats have kept cybersecurity teams on edge – these are vulnerabilities that attackers exploit before anyone even knows they exist. These threats leave no time for preparation, hence their name. But now, the game is changing, and not for the better. With artificial intelligence (AI) in the mix, zero-day dangers are evolving into something far more alarming: “zero hour” threats.

 In this blog, Craig Lusher, Product Principal at C8 Secure, explores how Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) platforms and Security Operations Centers (SOCs) allow organizations to adapt to emerging threats, maintain a robust cybersecurity posture and meet regulatory compliance.
In this blog, Craig Lusher, Product Principal at C8 Secure, explores how Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) platforms and Security Operations Centers (SOCs) allow organizations to adapt to emerging threats, maintain a robust cybersecurity posture and meet regulatory compliance.